[gravel_and_asphalt_calculator]
—————————–
Using a gravel and asphalt calculator is essential for accurately determining the amount of material required for your project, whether it’s a driveway, parking lot, or construction site. By entering the area and desired thickness, you can easily calculate the exact volume of gravel or asphalt needed, helping you avoid overordering and cutting costs. Calculating the right material volume ensures proper coverage, stability, and drainage, reducing the risk of premature damage and expensive repairs. With accurate calculations, you can plan for material costs and transportation, ensuring efficient project execution.
Understanding the Layers The Gravel and Asphalt Layer
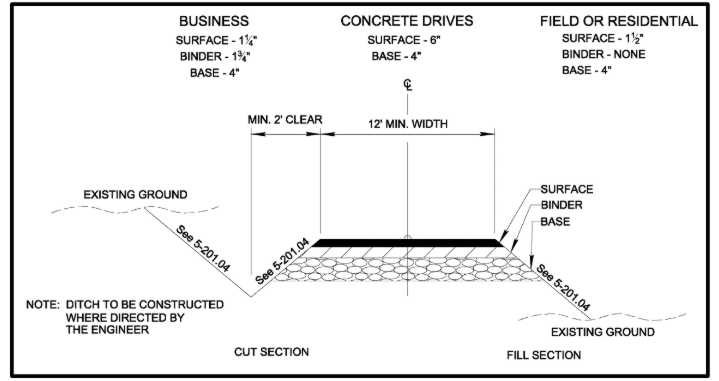
Base Layer (Gravel)
The base layer, commonly referred to as the gravel layer, serves as the foundation for your driveway. It provides stability and drainage, ensuring that the driveway can withstand the weight of vehicles and resist cracking or settling over time. The thickness of this layer typically ranges from 4 to 8 inches, depending on the soil conditions and the anticipated load.
Surface Layer (Asphalt)
The surface layer, or the asphalt layer, is the topmost layer that you’ll drive on. It provides a smooth, durable, and aesthetically pleasing surface. The thickness of this layer can vary from 2 to 4 inches, depending on the desired load-bearing capacity and the climate conditions in your area.
How do you calculate the amount of gravel needed?
Step 1: Measure the Driveway Area First, determine the total area of your driveway or project site by multiplying the length and width (both in feet) to get the square footage.
Step 2: Select Gravel Type and Depth Different gravel types serve different purposes. Common types include crushed stone, pea gravel, and gravel dust, each with varying costs and benefits. The standard depth for gravel layers is typically between 2 to 4 inches (0.17 to 0.33 feet), depending on the traffic load and soil conditions.
Step 3: Calculate Gravel Volume Use this formula to calculate the gravel volume: Gravel Volume (cubic feet) = Driveway Area (square feet) × Gravel Depth (feet)
For example, a 500 square foot driveway with a 3-inch (0.25 feet) gravel layer: Gravel Volume = 500 square feet × 0.25 feet = 125 cubic feet
To convert this into tons, multiply by the weight of gravel, which varies between 2,400 to 3,000 pounds per cubic yard.

How do you calculate the quantity of asphalt?
Step 1: Measure the Driveway Area Use the same area measurement calculated for the gravel section.
Step 2: Choose the Desired Asphalt Thickness Asphalt thickness typically ranges from 2 to 4 inches (0.17 to 0.33 feet), depending on traffic volume and environmental factors.
Step 3: Calculate the Asphalt Volume To calculate asphalt volume, apply the following formula: Asphalt Volume (cubic feet) = Driveway Area (square feet) × Asphalt Thickness (feet)
For instance, for a 500 square foot area with a 3-inch (0.25 feet) asphalt layer: Asphalt Volume = 500 square feet × 0.25 feet = 125 cubic feet
How do you convert asphalt volume to weight?
To determine the weight of the required asphalt, use the conversion factors for asphalt density. The weight of hot mix asphalt ranges from 145 to 165 pounds per cubic foot, while cold mix asphalt ranges from 125 to 145 pounds per cubic foot.
For example: If 125 cubic feet of hot mix asphalt is needed, and the weight is 150 pounds per cubic foot: Total Asphalt Weight = 125 cubic feet × 150 pounds/cubic foot = 18,750 pounds or approximately 9.38 tons.
Important Considerations for Driveway Calculations
Slope and Drainage A proper slope is essential to prevent water from accumulating near structures. Ensure a minimum slope of 1% (1/8 inch per foot) to direct water away from buildings and prevent damage.
Compaction Compaction is crucial for both gravel and asphalt layers to ensure stability and durability. Use a plate compactor or roller to compress each layer thoroughly, which will prevent future issues like cracking or shifting.
Edge Restraints To keep the driveway materials from spreading, install edge restraints such as concrete curbs or landscape edging.
Material Cost Breakdown
Gravel Costs
- Crushed Stone: $15 – $25 per ton
- Pea Gravel: $20 – $35 per ton
- Gravel Dust: $10 – $20 per ton
Asphalt Costs
- Hot Mix Asphalt: $80 – $120 per ton
- Cold Mix Asphalt: $60 – $90 per ton
These prices can fluctuate depending on location, material quality, and supplier. When planning a project, consider transportation costs and the overall cost of materials.
Can I use gravel alone without an asphalt layer for my driveway?
Yes, but asphalt provides better durability, a smoother surface, and easier maintenance.
How long does an asphalt driveway last?
An asphalt driveway can last 12 to 20 years with proper maintenance, depending on climate, usage, and materials.
Can I install gravel and asphalt myself?
Yes, but hiring professionals is recommended, especially for larger projects, to ensure correct compaction and durability.
Do I need to remove the existing driveway before installing a new one?
Yes, the old surface should be removed to avoid compromising the integrity of the new layers.
Can recycled asphalt be used for my driveway?
Yes, recycled asphalt can be used as long as it meets quality standards, offering a sustainable and cost-effective option.
Can I install a gravel driveway on a steep slope?
Yes, but proper drainage and erosion control measures are necessary to prevent gravel from washing away.
How do I calculate the materials for a curved driveway?
Divide the curved area into smaller sections, calculate each separately, and sum the results.
Can I use alternative materials like concrete or pavers?
Yes, but concrete or pavers may offer different benefits in terms of aesthetics and maintenance compared to asphalt.
Gravel and Asphalt for Road Maintenance
Assessing the Damaged Area
Step 1: Identify the Repair Zone
Determine the section needing repair, including potholes, cracks, or severely deteriorated areas.
Step 2: Measure the Repair Area
Use a tape measure or measuring wheel to measure length, width, and depth accurately.
Calculating Gravel and Asphalt Quantities for Road Repair
Use the same formulas as above to calculate the required gravel and asphalt volumes, factoring in the repair area’s square footage and desired layer thickness.
Gravel Weight Conversion Table
| Gravel Type | Weight per Cubic Yard (tons) |
|---|---|
| Crushed Stone | 1.4 – 1.7 |
| Gravel Dust | 1.6 – 1.9 |
| Recycled Concrete | 1.2 – 1.5 |
Asphalt Weight Conversion Table
| Asphalt Type | Weight per Cubic Yard (tons) |
|---|---|
| Hot Mix Asphalt | 2.1 – 2.5 |
| Cold Mix Asphalt | 1.8 – 2.2 |
